Human Heart
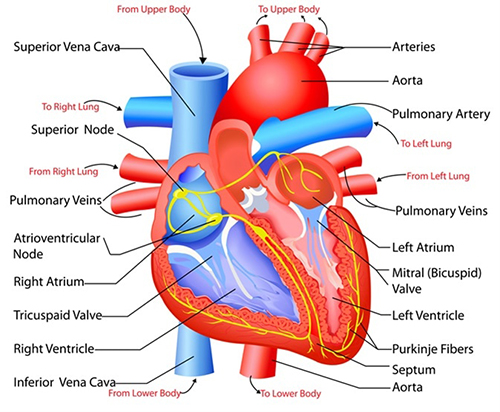
The heart is a muscular pump that provides the force necessary to circulate the blood to all the tissues in the body. Normal adult heart pumps about 5 liters of blood every minute throughout life. Its function is essential as tissues need a continuous supply of oxygen and nutrients and metabolic waste products have to be removed. Blood is the transport medium and heart is the organ that keeps the blood moving through the vessels.
The oxygenated blood flows out from the heart through aorta, which is the largest artery in the body. All the major arteries, which supply blood throughout the body, arise from aorta. Blood vessels called veins return the blood to the heart. After picking up oxygen from the lungs, the blood is pumped out to the body again. The heart receives its own supply of blood from a network of arteries called the coronary arteries.
Two major coronary arteries branch off from the aorta :
Right coronary artery & Left main coronary artery (RCA & LMCA) – Which supplies 20 – 30 % of the heart’s blood.
These major arteries branch into smaller arteries that supply blood to every part of the heart muscle.
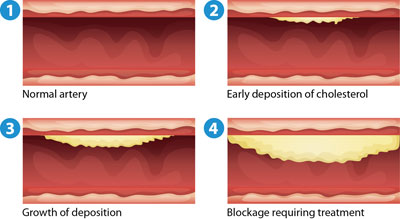
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease is the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries caused by atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis (sometimes called “hardening” or “clogging” of the arteries) is the buildup of cholesterol, and fatty deposits (called plaque) on the inner walls of the arteries that restricts blood flow to the heart. Without adequate blood, the heart becomes starved of oxygen and the vital nutrients it needs to work properly. This can cause chest pain called angina. When one or more of the coronary arteries are completely blocked, a heart attack (injury to the heart muscle) may occur.
Symptoms
The most common symptom of coronary artery disease is angina (also called angina pectoris). Angina is often referred to as chest pain. It is also described as chest discomfort, heaviness, tightness, pressure, aching, burning, numbness, fullness, or squeezing. It can be mistaken for indigestion or heartburn. Angina is usually felt in the chest, but may also be felt in the left shoulder, arms, neck, back or jaw.
- Pain or discomfort in other areas of the upper body including the arms, left shoulder, back, neck, jaw, or stomach
- Difficulty in breathing or shortness of breath
- Sweating or “cold sweat”
- Fullness, indigestion, or choking feeling (may feel like “heartburn”)
- Nausea or vomiting
- Light-headedness, dizziness, extreme weakness or anxiety
- Rapid or irregular heart beats
Remember
- Learn to identify your symptoms and the situations that cause them.
- If your chest pain (angina) lasts for more than 5 minutes and if you don’t have prescription for nitroglycerin – call for emergency help.
- If you have been prescribed nitro-glycerine and you experience angina, stop what you are doing and rest. Take one nitro-glycerine tablet and let it dissolve under your tongue, or if used in the spray form, spray it under your tongue. Wait for 5 minutes. If you still have angina after 5 minutes, call your doctor.
- Call your doctor if you begin to have new symptoms or if they become more frequent or severe.
Risk Factors
There are risk factor for heart disease: some are controllable, others are not.
Risk factors which are uncontrollable are:
- Sex (Male or Female)
- Older age
- Family history of heart disease
- Post-menopausal
Still, there are many risk factors that can be controlled. By making changes in your lifestyle, you can actually reduce your risk for heart disease.
Controllable Risk Factors Include:
- Smoking
- High LDL, or “bad” cholesterol and low HDL, or “good” cholesterol
- Uncontrolled hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Physical inactivity
- Obesity (more than 20% over one’s ideal body weight)
- Uncontrolled diabetes. Uncontrolled stress and anger.
- Uncontrolled stress and anger
Here are some ways you can reduce your risk of heart disease:
- Quit Smoking
- Improve cholesterol level
- Control high blood pressure
- Control diabetes
- Get Active
- Eat right
- Achieve and maintain a healthy weight
- Manage stress
Doctor may use various methods to diagnose CAD
- Electrocardiograph tests, such as an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) or exercise stress tests, to evaluate the electrical activity generated by the heart at rest and with activity. Echocardiogram involves a use of transducer which works on a sound wave to detect the problem with your heart; sound waves produced by the transducer are reflected back from the chest surface which are received again and sent to a computer to generate report.
- Laboratory Tests: include a number of blood tests used to diagnose and monitor treatment for heart disease.
- Coronary angiography performed by a cardiologist in a cardiac catheterisation lab; involves inserting catheters into the blood vessels of the heart in order to get a closer look at the coronary arteries. (most confirmatory test among all)
These tests help your doctor decide how to treat you
Treatment of CAD
Treatment of coronary artery disease is aimed at controlling symptoms and slowing or stopping the progression of disease. The method of treatment is based on many factors determined by your symptoms, a physical exam, and diagnostic testing. You may be asked to change the life style, physical activity and diet control. If the blockage is less than 70 percent, medications may be the first line of treatment and if greater than that you might be asked for angioplasty with or without stent or coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG).
To prevent damage to your heart muscle, do not delay seeking medical treatment.

